MySQL
MySQL
is a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) that runs as a
server providing multi-user access to a number of databases. For more
information on MySQL, you can visit their website at www.mysql.com.
Version
This documentation was written for MySQL 5.0.45 but may be usefull with other versions.How to install MySQL
- Install MySQL
yum install mysql-server mysql php-mysql
How to configure MySQL
- Set the MySQL service to start on boot
chkconfig --levels 235 mysqld on - Start the MySQL service
service mysqld start - Log into MySQL
mysql -u root - Set the root user password for all local domains
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('new-password');
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost.localdomain' = PASSWORD('new-password');
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'127.0.0.1' = PASSWORD('new-password'); - Drop the Any user
DROP USER ''@'localhost';DROP USER ''@'localhost.localdomain'; - Exit MySQL
exit
- [root@www ~]#[root@www ~]#
yum -y install mysql-server/etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld start
Initializing MySQL database: Installing MySQL system tables... OK Filling help tables... OK To start mysqld at boot time you have to copy support-files/mysql.server to the right place for your system PLEASE REMEMBER TO SET A PASSWORD FOR THE MySQL root USER ! To do so, start the server, then issue the following commands: /usr/bin/mysqladmin -u root password 'new-password' /usr/bin/mysqladmin -u root -h www.server.world password 'new-password' Alternatively you can run: /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation which will also give you the option of removing the test databases and anonymous user created by default. This is strongly recommended for production servers. See the manual for more instructions. You can start the MySQL daemon with: cd /usr ; /usr/bin/mysqld_safe & You can test the MySQL daemon with mysql-test-run.pl cd mysql-test ; perl mysql-test-run.pl Please report any problems with the /usr/bin/mysqlbug script! The latest information about MySQL is available on the web at http://www.mysql.com Support MySQL by buying support/licenses at http://shop.mysql.com [ OK ] Starting MySQL: [ OK ]
[root@www ~]#chkconfig mysqld on
[root@www ~]#mysql -u root# login to MySQL
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 2 Server version: 5.0.77 Source distribution Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the buffer.
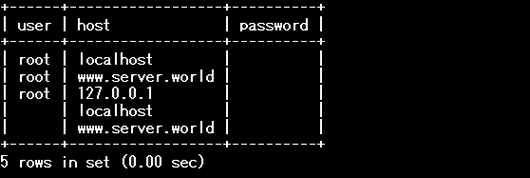
# show user info
mysql>select user,host,password from mysql.user;
 # set root password
# set root password
mysql>
set password for root@localhost=password('password');
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)# set root password
mysql>
set password for root@'127.0.0.1'=password('password');
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)# set root password
mysql>
set password for root@'www.server.world'=password('password');
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql># delete anonymous users
mysql>
delete from mysql.user where user='';
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)select user,host,password from mysql.user;
mysql>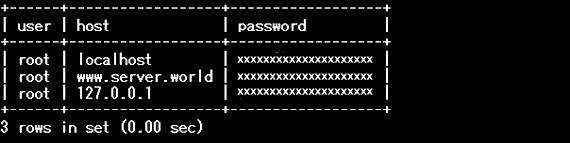 exit# quit
exit# quit
Bye
[root@www ~]#mysql -u root -p# login as root
Enter password:# MySQL root password
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 3 Server version: 5.0.77 Source distribution Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the buffer.
mysql>exit
Bye

No comments:
Post a Comment